For those of you confused, website structure is not the same as website design. Instead, it refers to how all the individual pages on your website link together.
The various pages on your website should link together in a way that makes logical sense so that both a user and a crawler can navigate around your site easily. Some of the structural elements that impact SEO include:
- Page URLs
- Duplicate URLs
- Site Navigation
- Structured Markup Data
- Featured Snippets
- Mobile Optimisation
How to Format Your Page URLs
Every page on your website should have a unique URL. This tells users and search engines that each page contains different content. You may even notice that some URLs start with https://, while others only http://. Google prefers websites using https://, as it suggests that a website is secure and safe for users to share their personal information if required. You can do this by purchasing an SSL certificate for your website.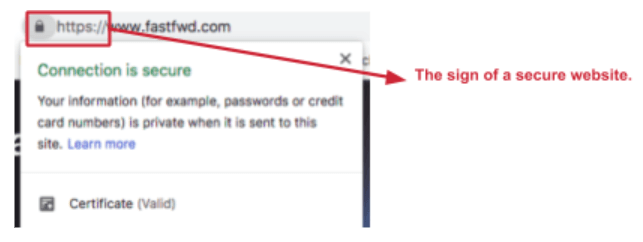
The main reason for formatting your URLs correctly relates to user experience. Imagine having a super long URL with numbers and other characters that make no sense, now compare it to a clean, simple URL:
https://example.com/pub/post?ID=32=10+dfgn23vewer321=t#apps
https://example.com/blog/cool-apps-to-improve-productivity
From a user perspective, you are likely to click on the second one, as you know exactly what you’ll get when you open the link. Having a clear URL is also good for when users are sharing your website link with others in emails or forums. If you received an email with the first link included, you would be inclined to open it. On the other hand, the second link looks much safer to click and view. From an SEO point of view, URL structure itself is considered to be a minor factor in ranking. But including keywords in your URL can improve your site’s visibility to a certain extent, as long as it does not compromise user experience.
To help you out, here are a couple of tips for formatting your page’s URL:
- Keep URLs short and clean (avoid unnecessary characters)
- Include keywords, but not too many
- Avoid using UTM parameters if it makes the URL look long and weird
- Ideally, create your URL from the page title
- You do not need to include stop words (and, or, the, a etc.)
- Avoid changing page URLs after a page has been published live
How to Deal With Duplicate URLs
Another important thing to remember (and most people do forget) is that every website has different versions of their domain, see some examples below:
http://example.com/
http://www.example.com/
http://example.com/index.php
http://www.example.com/index.php
https://example.com
https://www.example.com
These domains themselves may slightly look different, but the content on the page looks exactly the same. Why is this an issue for your website? The biggest problem with this is; the split in reputation, as Google will see each domain version as a separate site. So instead of one domain getting all the traffic, you are spreading your traffic thinly across multiple variations of the same content. Google will also see all these versions of the domain as duplicate content and will start crawling your website less often as a result.
To avoid this issue, you should define a canonical URL for your duplicate web pages. A canonical URL is a page that Google sees as the primary or preferred page from a set of duplicate pages. For example, Google will need to choose a canonical URL from the following: http://example.com/ and http://example.com/index.php.Google uses the canonical URL to evaluate the quality of the page and to show it in the search results page. In some cases even if you set a Canonical URL, Google may override this setting.
For example, if you are using a mobile, the mobile version of the webpage will automatically get set as the Canonical URL even if the desktop version is marked as a canonical:
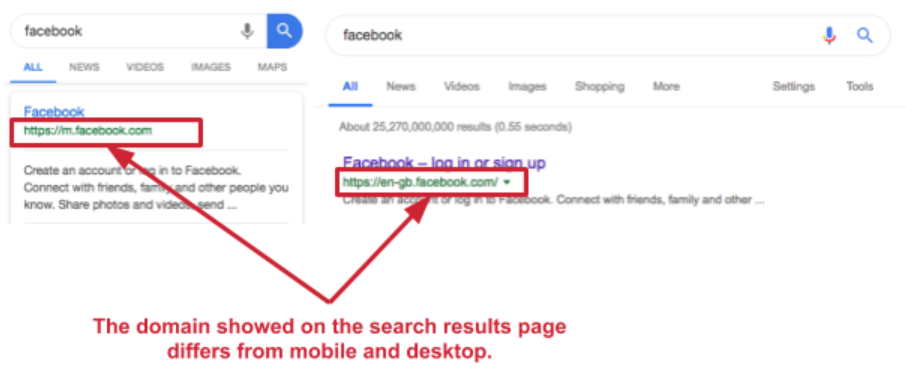
If a canonical URL is not set, Google will make the choice for you based on factors, such as quality of content. Other duplicate pages will therefore be crawled less often to reduce Googlebot loading on your site.
If you want to control the decision of which page is canonical on your website, you can do the following:
- Choose a preferred version of your domain in search console
- Set up 301 redirects for duplicate pages
- Use the rel=”canonical” element on the duplicate page
For more information on Canonical URLs and how to redirect duplicate pages, please read Google’s guide on duplicate URLs.
Is Navigation Important for SEO?
Your website’s navigation is the first place a user will look when they are trying to find something on your website. If there is an important page or section on your site that you want people to visit make sure you clearly include it in your navigation. Just take a look at Etsy’s website menu, if you’re a fan of art you’ll definitely know where to find different types of artwork for your home:
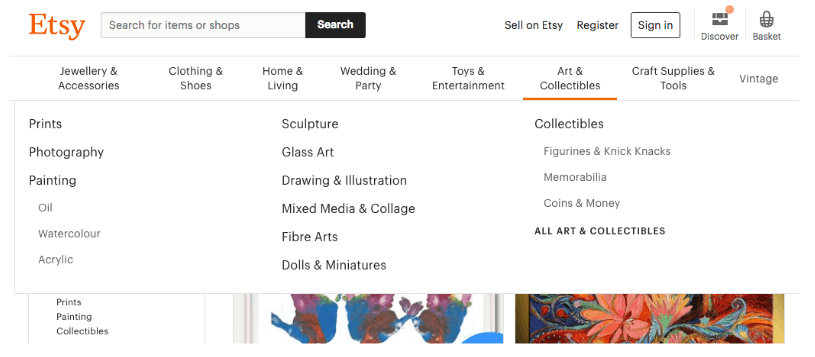
But what role does your website’s navigation play in SEO? Well, a good site navigation makes it easier for Google to crawl and index the pages on your site. A good navigation also means that users will easily be able to navigate to other sections of your website, increasing the time they spend on your website. This means a lower bounce rate, which all shows Google that your site offers quality content.
If you have a relatively small website, then your navigation items will be easy to plan out. However, if for instance, you have a large eCommerce store, planning out your site navigation can get very confusing! The best way to deal with a site that has thousands of pages is to categorise these pages under a suitable hub or category page which your users can click-through to find what they are looking for. Mapping a navigation flowchart (or sitemap) can help you see how easy your navigation is to understand and navigate through. Below is an example if a navigation flowchart for an eCommerce site that sells artwork:
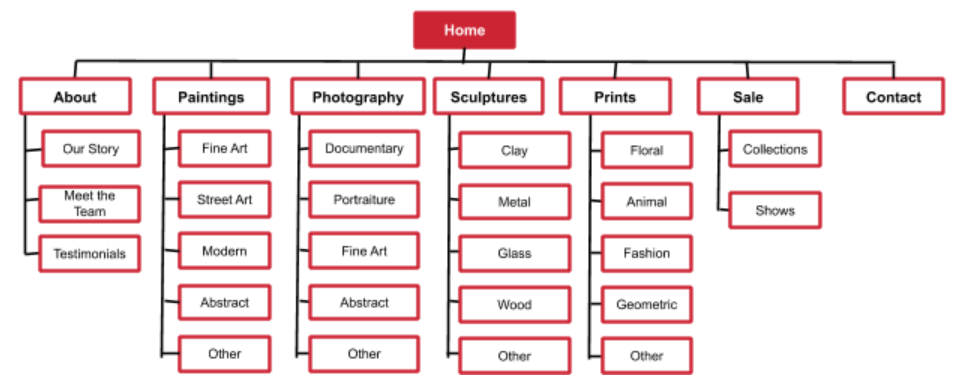
Another useful feature to include on your website is breadcrumbs. Breadcrumbs are internal links, which you may find at the top or bottom of a page. They allow users to easily go back to a previous section of your site. Breadcrumbs normally start from your homepage and then go deeper into a particular category or topic (see the example below):
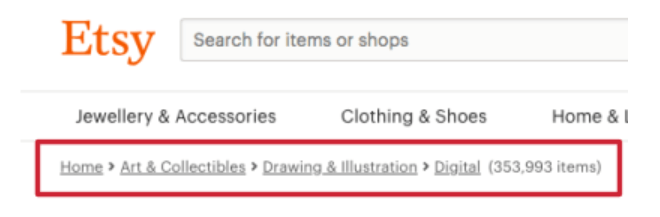
Both breadcrumbs and your site’s navigation help users and search engines if done right! Here are a couple of tips on how to structure your site’s navigation:
- Avoid using images or animations as buttons in your navigation.
- Do not list all your pages in the navigation, categorise them in appropriate category pages.
- Keep your navigation clean with 1 or 2 sub-sections at the most.
- Keep navigation link text short and clear.
- Make sure there are no broken links in your navigation.
How to Get Structured Data for Your Site
Structured data is a code that you add to your pages to help Google understand the content of your page. When Google truly understands your content it will reward you by displaying extra content on the search results page, otherwise known as a rich snippet.
The benefit of this extra content is that it will make your website look more reputable compared to your competitors (and make your results stand out from the rest). This means that more people will click on your result compared to competitors and as more people click on your result, Google will see that people prefer your result over others. This then improves your ranking in the long term. Take a look at the example below of a review rich snippet:
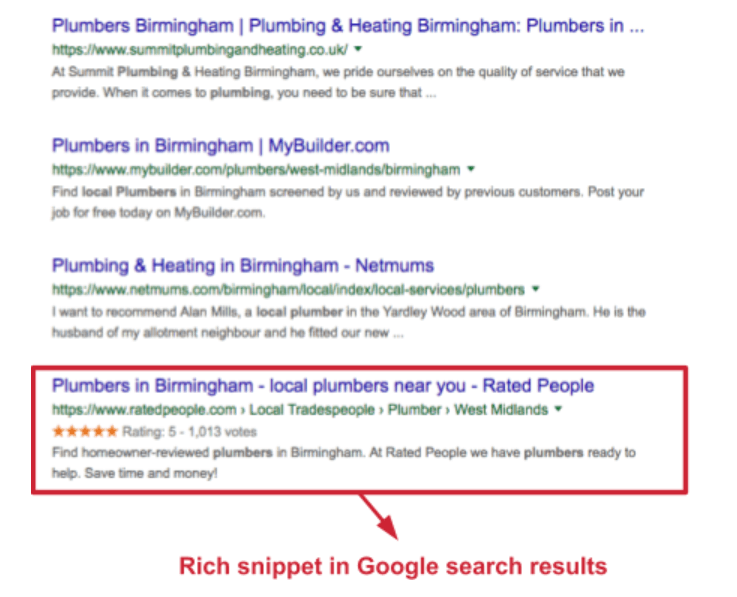
Your webpages can have all sorts of rich snippets, such as the following:
- Article
- Event
- Local Business
- Logo
- Recipe
- Review
See Google’s search gallery for a full list of rich snippets. If you would like to add structured markup data to your site we suggest using Google’s data highlighter tool or the markup helper, especially if you are new to this technical stuff. Once you have gone through the tool and added markup to some of your pages, you can test your markup out for any errors, using Google’s structured data testing tool
Please note there is no guarantee that even if you add the code or use the tools above to add structured data to your site that Google will give you a rich snippet. Getting a rich snippet depends on the quality of your content and its relevance to the searcher.
Here are some tips for adding structured data to your website:
- Always check your markup for any errors (you can use the tester tool mentioned before).
- Do not change your website’s code, if you don’t know what you’re doing (ask a developer to help you).
- Keep track of your marked up pages (you can use the Enhancement reports in search console).
- Do not add markup which is not relevant to your page, such as adding a recipe markup when your site has no recipes.
- Avoid adding incomplete markups to a site where important information required for that markup is missing.
Get Your Site Featured With Featured Snippets
Another way to make your results really pop on the search results page is featured snippets. Featured snippets are results that Google features at the top of some search results (below the ads). Featured snippets have been created to answer the user’s query as quickly as possible. Take a look at this example:
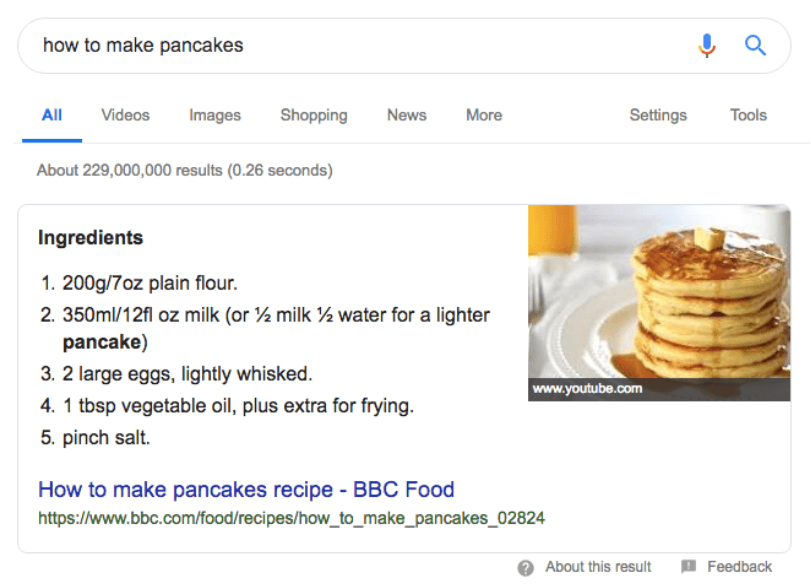
If your site is featured in a featured snippet, you could get more brand exposure and a significant boost in click-throughs. There are many types of featured snippets Google uses depending on the search query:
- List (screenshot above)
- Paragraph (an extract of relevant text from your page)
- Table
Please note, you can not mark your pages as a featured snippet. It is up to Google to show your result as a featured snippet. If you would like to opt-out of featured snippets, you can use the tag on your page and this will remove all snippets of your page in the search results. If you want to improve the chances of your site being featured at the top, here are some tips you can follow:
- Focus on a specific keyword or phrase that you are ranking in the top 10 for.
- Try looking at question-type queries (i.e. how, what, why etc.).
- Also look at long-tail, informational keywords for featured snippet opportunities (you might find this post on how to do keyword research useful).
- Focus on keywords that already have a featured snippet in the results page.
- Try improving on the content of a competitor with a featured snippet.
Is Your Website Mobile-Friendly?
On average, up to 70% of web traffic comes from a mobile device. In most cases, the desktop version of your site would be impossible to view on a mobile device. Therefore it is essential that your site is optimised for mobile devices. Below is an example of how a mobile site can differ in appearance compared to a desktop site:
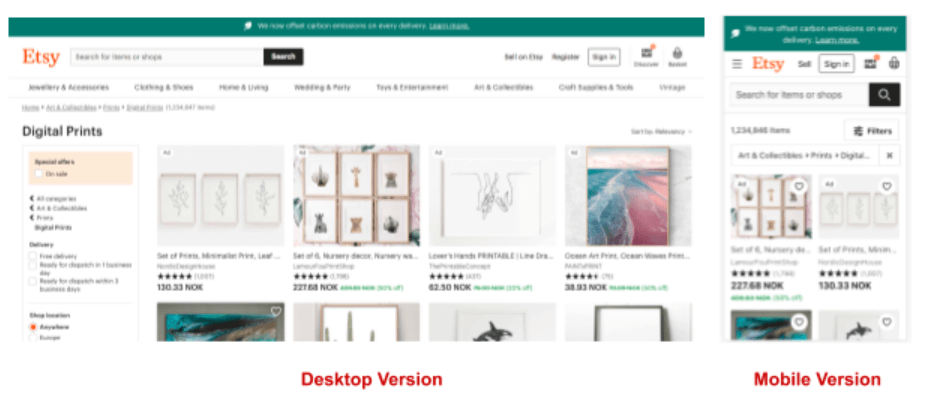
If you are unsure whether your site is mobile optimised, you can use Google’s mobile-friendly test to see how optimised your site is for mobiles. You can also refer to the mobile usability report inside Search Console to see what issues are affecting your site on mobile. If your current site is not mobile responsive or you would like an update, then Fastfwd can help create a mobile-friendly site that works for your business. Here are a couple of tips for ensuring your site is fully mobile optimised:
- Make sure you test all areas of your website on mobile, desktop and tablet to ensure everything looks and works fine.
- Use the Google mobile-friendly test to optimise your site for mobile further.
- Hire a professional to create a mobile site that converts visitors.