The first step to improving your position in Google is to understand how Google actually views your website. Your ultimate goal is to make sure that Google views your content the same way an everyday user will view it. The URL inspection tool located in the search console is a great way to determine how Google views your content. It can also help fix any indexing issues with your site or webpages.
Using the URL inspection tool we can see the difference between how we (as humans) would see a webpage compared to Google’s view:
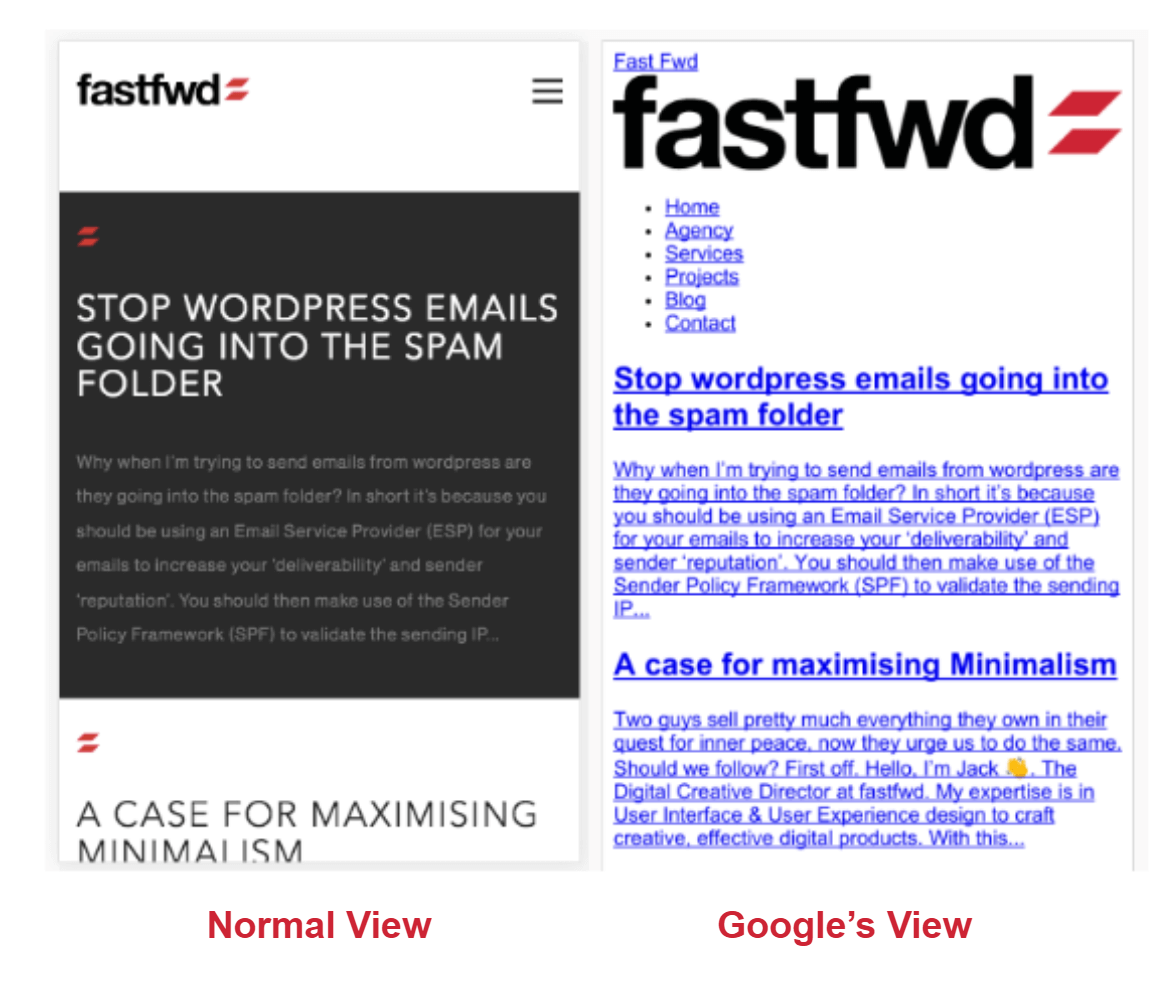
As you can see the background colour, along with some icons are missing from Google’s view. However, the important information, such as headings, text and logo are still visible. This is the type of information that gives Google a clear idea of what a page is about. Using this information Google is able to index a web page for different search queries made by users.
There are a number of key elements that help Google understand your site’s content, these include some of the following (each is explained below):
- Page Titles
- Meta Descriptions
- Heading Tags
- Image Alt Tags
- Link Text
- Links
Of course, you should never forget the non-technical, human side of content which is to create content that keeps your readers hooked and engaged. This actually is more important than following the technical rules of on-page SEO. For some great tips on creating content for your site, we suggest you read this post on five non-technical tips for your site’s content
How to Write SEO Friendly Page Titles
Page titles inform search engines about what each page is about. On the search results page, this is the first line of text above your URL:
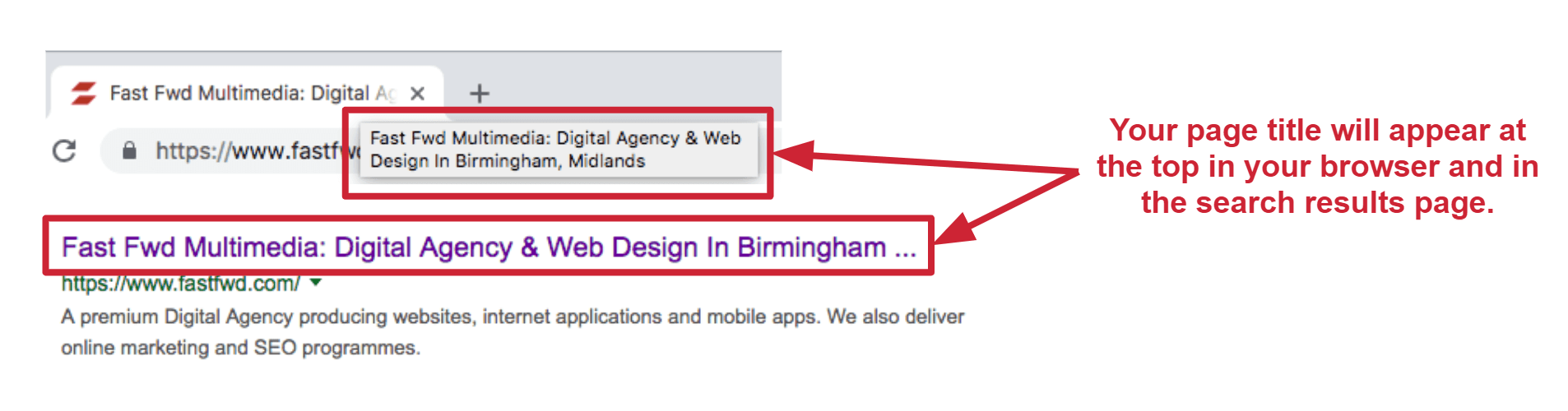
They are normally between 50 to 60 characters (any longer and they’ll get cut off on the results page). Each page on your website should have a unique page title. Normally the page title includes your business name and a couple of words to describe the page. It can also include your physical location if you have one.
Here are a couple of tips for creating effective page titles:
- Create unique page titles for every page on your site
- Keep your titles short, but descriptive
- Do not stuff your page titles with loads of keywords
- Make sure your page title describes your page clearly
- If you have a focus or target keyword, try to include this towards the beginning
- Keep page titles under 60 characters
How to Write Effective Meta Descriptions
A meta description is a short paragraph that appears in the search results under the page title and URL. It is normally between 50 to 300 characters long, after 300 characters your text may get cut off. The aim of a meta description is to offer search engines an overview of what your page is about.
Please note, that Google may not always show your written meta-description. Instead, it might choose another, more relevant snippet from your page’s content based on the user’s search query. However, a meta description is still very important for your web pages, in case Google can not find any relevant text in your page’s content. The example below shows how Google will automatically pull out a relevant snippet of text from your site if your current meta-description is not relevant to the user’s search:
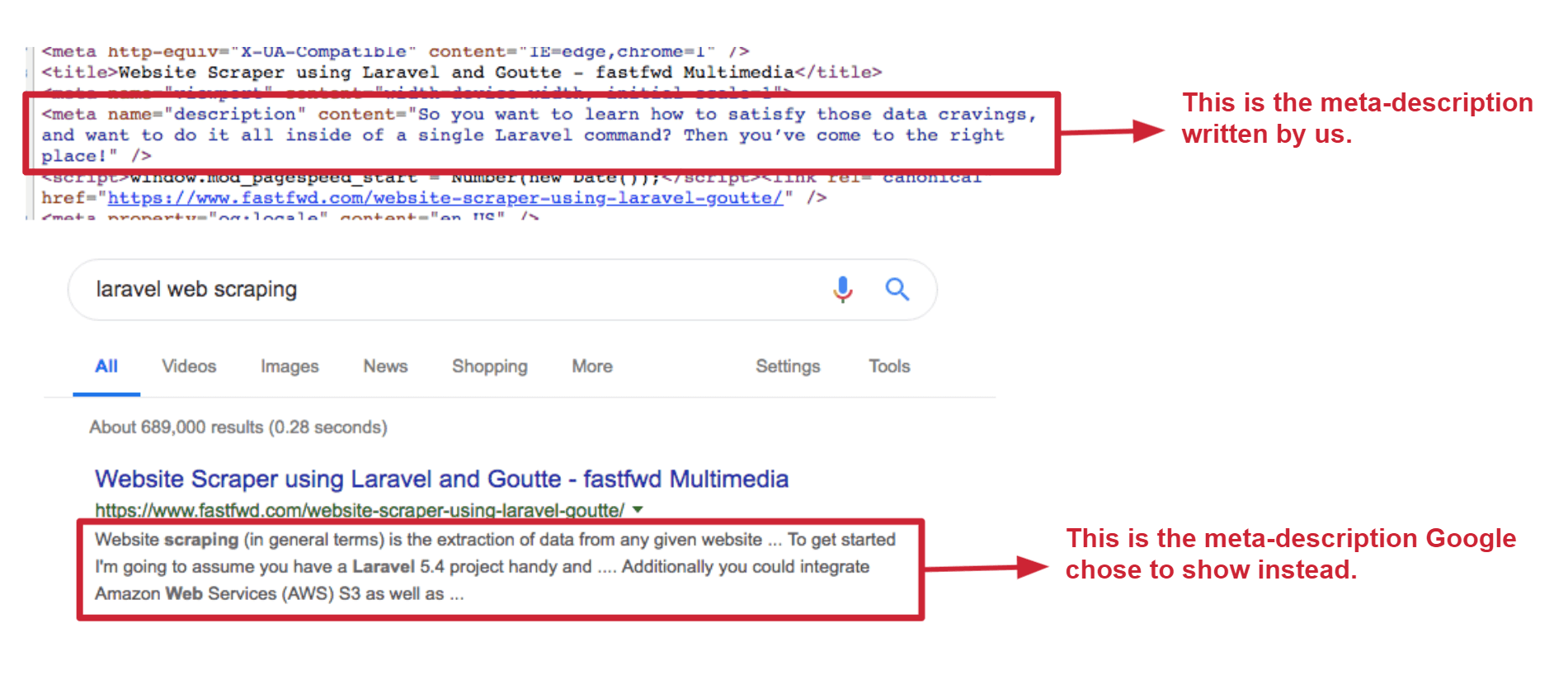
A well-written meta-description can also encourage people to click-through onto your website from the search results page. Here are some tips for creating an effective meta description:
- Accurately summarise the content of your page
- Create unique meta descriptions for every page on your site
- Keep meta descriptions around 160 characters
- Never stuff your meta description with a bunch of keywords
- Never copy and paste your entire page’s content into the meta description
How to Use Heading Tags Effectively
Headings just like chapters in books, act as a visual cue for readers as to the type of content they will find in that section. Headings also make navigating through long content easier and more manageable. You might have noticed that there are multiple sizes to headings, such as an H1 tag is the largest and an H2 tag would be smaller and so on. Here is a typical structure that might be used for headings on your page:
H1: 10 brilliant apps
H2: App Name
H3: Pros
H3: Cons
H3: Summary
H2: App Name
H3: Pros
H3: Cons
H3: Summary
H2: Wrapping it up
Good headings grab attention and encourage the reader to read on. Here are some tips on how to use headings effectively in your content:
- Do not use too many headings or subheadings in your content
- Make sure your headings are short and informative
- You can use H4, H5 and onwards, but it’s best to stick to H2 and H3 tags
- Your page should only have one H1 tag
- Keep your subheadings consistent throughout in length and format
How to Create Effective Alt Tags for Images
Alt tags are extremely important for search engines. Why? Because search engines can’t actually see what your image is showing, they can only read text content. Therefore if you only include an image with no alt tag, a search engine will only see an image but not know what this image is about. Another reason for including alt tags is for when a user’s browser can not show the image. So instead, it will show the alt tag or alternative text to describe the image:

It is also worth keeping in mind that image search results are heavily influenced by alt tags:

When adding alt tags to your images, please bear in mind the following tips:
- Try not to use images as links in your website’s navigation
- Keep your alt tags short and descriptive
- Never include whole sentences as alt tags
- Avoid keyword stuffing your alt tags
- Never use generic file names as alt tags or even as file names (e.g. image_1.jpg or pic_34234.jpg)
How to Create Effective Anchor Text
Link text or anchor text is text contained in a hyperlink on your website. It might link to a page on your website (internal link) or a page on someone else’s website (external link). Link text helps search engines understand what the page you are linking to is about. It also helps your users navigate to pages on your site with similar or relevant content.
The common mistake most people make is to use “click here” or “page” as a link text. Both these examples do not tell the user or search engine what the page you’re linking to is about. To make sure your link text is effective, here are some tips to follow:
- Make sure your link text looks clickable (i.e. different colour from other text on the page)
- Make sure your link text is short (between 1 – 5 words)
- Do not overuse keywords as link text
- Do not create unnecessary links which are not relevant to the page
- Make sure your link text is descriptive of the page you are linking to
Best Practices for Including Links in Your Content
Including links in your content is important for both readers and search engines. From a reader’s perspective, they can find and read relevant content easily with the help of links inside your content. And from a technical perspective, internal links help search engines find and index other pages on your site and help keep users on your site (which translates to Google as a quality site).
An important thing to consider about including external links is that every time you include an external link you are passing some of your site’s ‘reputation’ to that website. In other words, you are endorsing that site’s content and telling Google that you recommend this content. Therefore it is important to check the quality of the site you are linking to. As a poor quality website, with irrelevant content, could negatively impact your site’s reputation. If you would like Google to ignore the external links on your webpage, you could use the “nofollow” attribute in the link or in thesection of your page:
An example of when the “nofollow” attribute would be useful is if you have a blog with a commenting section. Whether you moderate the comments for external links or not, including the “nofollow” attribute will prevent other sites (especially comment spammers) from taking your reputation without permission.Here are some best practices for including links in your content:
- Try to include between 2 to 3 internal links to other content on your site
- Include a relevant amount of external links to trustworthy sources
- Make sure you use the ‘nofollow’ attribute in the comments section of your site
- Make sure the link you use are highly relevant to your content/li>